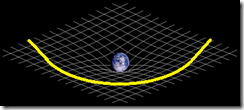
1. ModelThis is modeled using a marble on a sheet of rubber. The marble deforms the sheet, forming the curve.
Curved Space-Time
(Courtesy online.physics.uiuc.edu)
If you place another marble on the rubber sheet, both marbles will eventually come together. If you roll a second marble, it will curve around the first marble.
Moon Attracted to Earth
(Courtesy LesToilesDeLUnivers.fr)
Additionally, light bends around celestial bodies because of the curvature of space.
Light Bending
Observation and Expectation
Experiments have shown that light does indeed curve around celestial bodies. During an eclipse, it was shown that light from distant stars was bending around the sun from.
According to theory, light has no mass, which is why the only way for light to curve is because space is curved.
A Critical Flaw
This model seems to explain everything, but it is fundamentally flawed - It only works on Earth.
If you take the model into outer space, it stops working. Objects still bend when travelling on the surface, but they no longer attract each other.
This can mean one of two things: either the model is incorrect, or there is a force external to the universe and affecting the universe. Either way, we haven’t yet discovered the true nature of gravity.
A force is acting perpendicularly to our Universe.
This force pushes mass downwards, curving space.
A second mass then curves around the first when rolled, as expected.
Rainbow Gravity
Recently an interesting theory has appeared. It's called Rainbow Gravity. According to the theory gravity affects different wavelengths of light, like a prism. Large scale experiments are currently under way to see if the theory is valid.
If the only reason light curves is because space is curved, then clearly Rainbow Gravity is wrong.
But what if Rainbow Gravity is correct?
Energy as Mass
From Wikipedia.org:
- Newton's law of universal gravitation states that any two bodies in the universe attract each other with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
Mass of Earth: 5,973,600,000,000,000,000,000,000 kg
Diameter of Earth at equator: 12,750 km
6.673×10−11 × ME × s
Force at surface of
http://www.dummies.com/how-to/content/how-to-calculate-the-force-of-gravity-on-the-earth.html